†: undergrad, +: highschooler
Osprey🪶: A Reference Framework for Online Grooming Detection (2023 - Now)
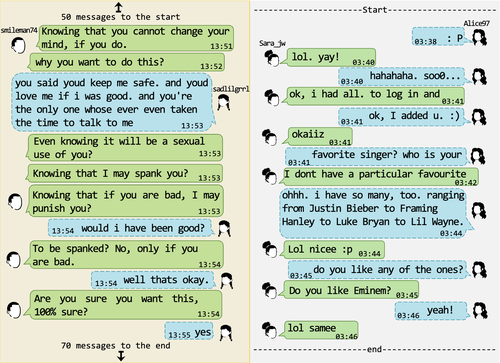
With the prevalence of more technology, minors access it before they are of legal age and with little cognitive development, facing an alarming problem of engaging with predators in online grooming. Through grooming, the sexual predator tries to form an emotional relationship with a minor to get her trust and make her engage in sexual activities afterwards. Recent stats show that 57% of girls and 48% of boys have experienced at least one online grooming, with some regions like north america and western europe being even higher. Meanwhile, crimes involving minors are underreported for lack of awareness, support, or trust in authorities, fear of retaliation from the predator or legal repercussions, and distress of being judged or blamed, among others. Such proceedings have stressed the development of computational models that plug into an online chat environment and help warn minors, parents or police of such incidents while preserving the minor's privacy. In many cases of online grooming, the predators mix explicit textual remarks to give the minor a feeling of endearment and to lure her into their trap while going through several stages. Such remarks can be extracted by natural language processing techniques and tapped into machine learning models to detect predators or predatory conversations. To this end, we have formulated online grooming detection problem as a Boolean text classification task and have tackled it through machine learning models. We contribute Osprey🪶, an open-source benchmark library to support a standard pipeline and experimental details, incorporating canonical neural models and a variety of vector representation learning for conversations while accommodating new models and training datasets.
- H. Waezi, H. Fani; Enhancing Online Grooming Detection via Backtranslation Augmentation. In the 31st International Conference on Computational Linguistics (COLING), 2025.
pdf doi git reviews ppt video - H. Waezi, R. Barzegar, H. Fani; Osprey🪶: A Reference Framework for Online Grooming Detection via Neural Models and Conversation Features. In the 33rd ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (CIKM), 2024.
pdf doi git reviews
RePair: An Extensible Toolkit to Generate Large-Scale Datasets for Query Refinement via Transformers (2022 - Now)
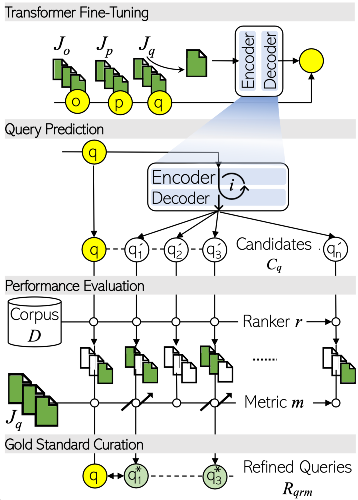
Search engines have difficulty searching into knowledge repositories since they are not tailored to the users' information needs. User's queries are, more often than not, under-specified that also retrieve irrelevant documents. Query refinement, also known as query reformulation or suggesetion, is the process of transforming users' queries into new refined versions without semantic drift to enhance the relevance of search results. Prior query refiners have been benchmarked on web retrieval datasets following weak assumptions that users' input queries improve gradually within a search session. To fill the gap, we contribute RePair, an open-source configurable toolkit to generate large-scale gold-standard benchmark datasets from a variety of domains for the task of query refinement.
- Z. Taheri, Z. Kobti, H. Fani; Comparative Study of Query Types on Query Refinement. The 2025 International Conference on Natural Language Processing and Information Retrieval (NLPIR), 2025.
pdf git reviews - Z. Taheri, M. Saeedi, Z. Kobti, H. Fani; Information Sources for Query Refinement: A Comprehensive Survey. The 2025 International Conference on Natural Language Processing and Information Retrieval (NLPIR), 2025.
pdf git major revisions minor revisions - Z. Taheri, M. Saeedi, Z. Kobti, H. Fani; A Survey of Query Refinement Techniques: From Neural Architectures to Practical Applications. International Journal of Computer Applications (IJCA), 2025.
pdf git minor revisions minor revisions - D. Rajaei, Z. Taheri, H. Fani; No Query Left Behind: Query Refinement via Backtranslation. In the 33rd ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (CIKM), 2024.
pdf doi git reviews video - D. Rajaei, Z. Taheri, H. Fani; Enhancing RAG's Retrieval via Query Backtranslations. In the 25th International Web Information Systems Engineering (WISE), 2024.
pdf doi git reviews ppt - Y. Lakshmi Narayanan, H. Fani; RePair My Queries: Personalized Query Reformulation via Conditional Transformers. In the 25th International Web Information Systems Engineering (WISE), 2024.
pdf doi git reviews ppt - Y. Lakshmi Narayanan, H. Fani; RePair: An Extensible Toolkit to Generate Large-Scale Datasets for Query Refinement via Transformers. In the 32nd ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (CIKM), 2023.
pdf doi git reviews
LADy💃: Latent Aspect Detection from Online Unsolicited Customer Reviews (2022 - Now)
Within the context of review analytics, aspects are the features of products and services at which customers target their opinions and sentiments. Aspect detection helps product owners and service providers to identify shortcomings and prioritize customers' needs,and hence, maintain revenues and mitigate customer churn. Existing methods focus on detecting the surface form of an aspect by training supervised learning methods that fall short when aspects are latent in reviews. In this project, we propose methods to extract latent occurrences of aspects.
- F. Hemmatizadeh, C. Wong†, A. Yu+, H. Fani; LADy: A Benchmark Toolkit for Latent Aspect Detection Enriched with Backtranslation Augmentation. The 47th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval (SIGIR), 2024.
pdf doi git reviews - F. Hemmatizadeh, C. Wong†, A. Yu+, H. Fani; Latent Aspect Detection via Backtranslation Augmentation. In the 32nd ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (CIKM), 2023.
pdf doi git reviews video - A. Mansouri, H. Fani; Latent Aspect Detection from Online Unsolicited Customer Reviews, 2022.
pdf
Adila: Fairness-Aware Team Formation (2022 - Now)
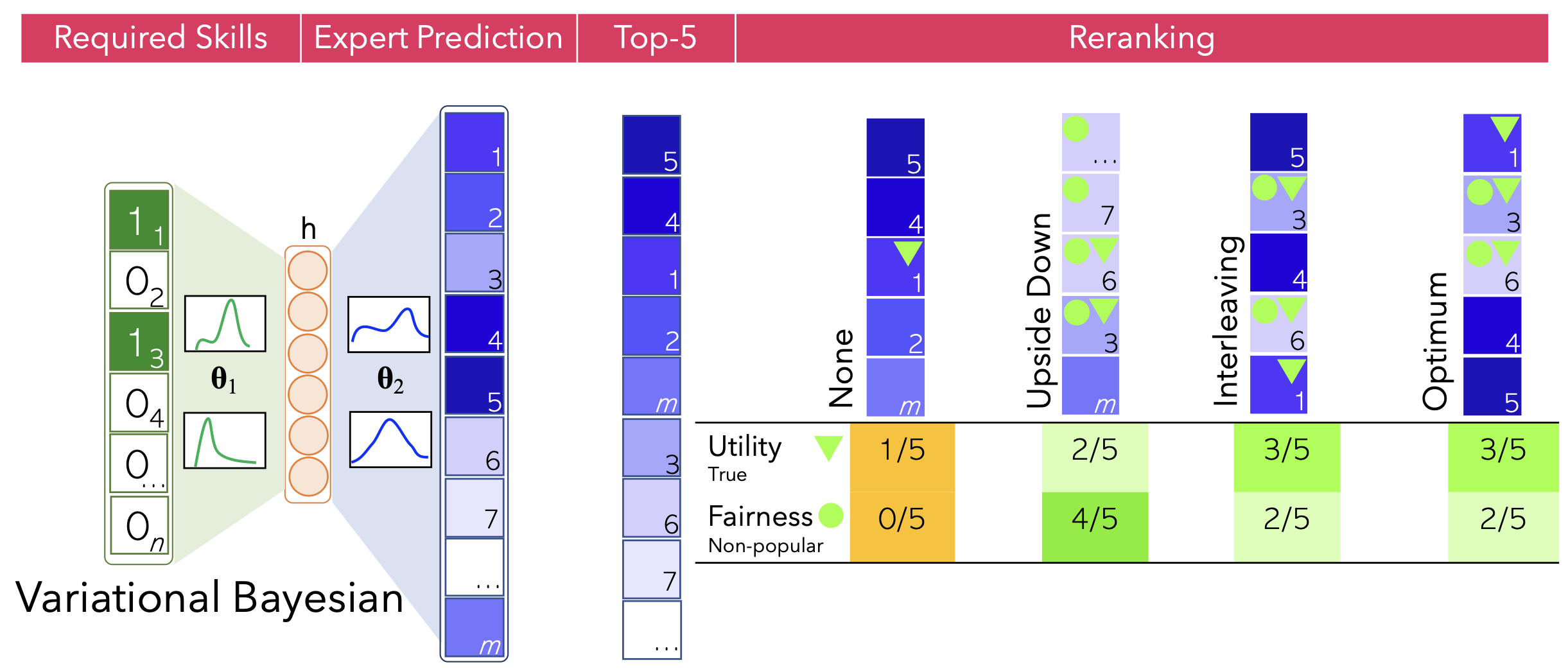
Team Formation aims to automate forming teams of experts who can successfully solve difficult tasks. While state-of-the-art neural team formation methods are able to efficiently analyze massive collections of experts to form effective collaborative teams, they largely ignore the fairness in recommended teams of experts. Fairness breeds innovation and increases teams' success by enabling a stronger sense of community, reducing conflict, and stimulating more creative thinking. In Adila, we study the application of fairness-aware team formation algorithms to mitigate the potential biases in the neural team formation models.
-
R. Moasses, D. Rajaei, H. Loghmani, M. Saeedi, H. Fani; vivafemme: Mitigating Gender Bias in Neural Team Recommendation via Female-Advocate Loss Regularization. The 5th International Workshop on Algorithmic Bias in Search and Recommendation, Colocated with the 47th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval (BIAS-SIGIR), 2024.
pdf doi git reviews - H. Loghmani, H. Fani; Bootless Application of Greedy Re-ranking Algorithms in Fair Neural Team Formation. In the 4th International Workshop on Algorithmic Bias in Search and Recommendation, Colocated with the 45th European Conference on Information Retrieval (BIAS-ECIR), 2023.
pdf doi git reviews video
OpeNTF: Neural Team Formation (2021 - Now)
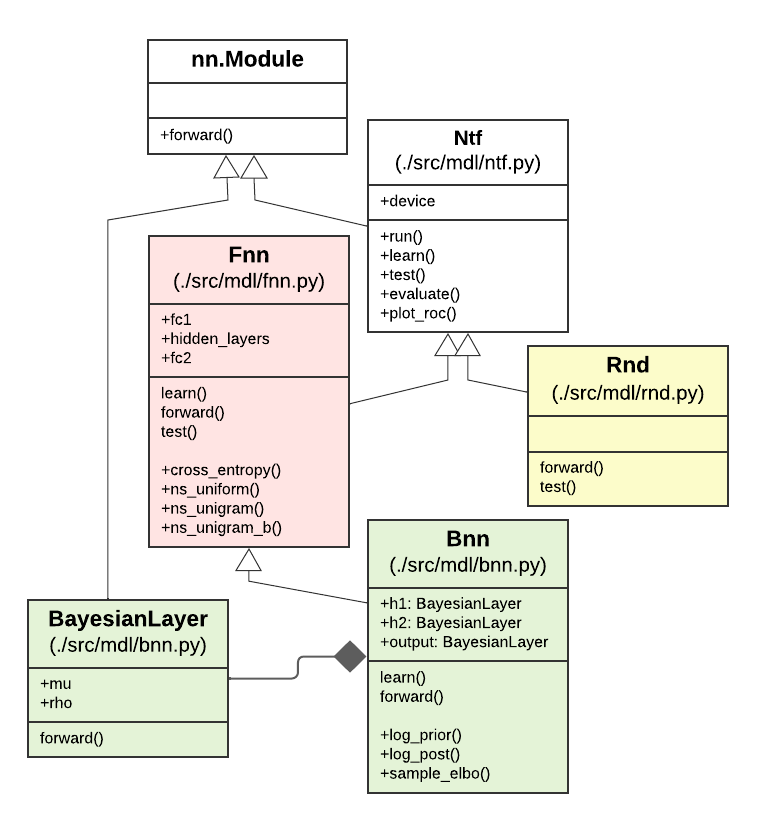
Collaborative teams are the primary vehicle for coordinating experts with diverse skills needed for a particular collaborative project, and Team Formation (TF) has firsthand effects on creating organizational performance. We propose neural machine learning approaches to Team Formation. We will train neural models that would learn relationships among experts and their social attributes in vector space. Wherein, we consider all past (un)successful team compositions as training samples to predict future teams and the team's level of success. Therefore, we bring efficiency while enhancing efficacy due to the inherently iterative and online learning procedure in neural architectures.
- M. Saeedi, Z. Kobti, H. Fani; Learning Collaborative Teams via Social Information Retrieval. In the 2026 ACM Web Conference (WWW), 2026.
pdf doi git reviews - M. Saeedi, H. Fani; Neural Shifts in Collaborative Team Recommendation. In the 34th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (CIKM), 2025.
pdf doi git reviews - M. Saeedi, H. Hosseini, C. Wong†, H. Fani; A Survey of Subgraph Optimization for Expert Team Formation. ACM Computing Survey (CSUR), 2025.
pdf doi git major revisions major revisions minor revisions - K. Thang, H. Hosseini, H. Fani; Translative Neural Team Recommendation: From Multilabel Classification to Sequence Prediction. In the 48th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval (SIGIR), 2025.
pdf doi git reviews poster - R. Barzegar, M. Kurepa+♥, H. Fani; Adaptive Loss-based Curricula for Neural Team Recommendation. In the 18th International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining (WSDM), 2025.
pdf doi git reviews - M. Saeedi, C. Wong†, H. Fani; Bridging Historical Subgraph Optimization and Modern Graph Neural Network Approaches in Team Recommendations. In the 18th International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining (WSDM), 2025.
pdf doi git reviews ppt - H. Fani, R. Barzegar, A. Dashti, M. Saeedi; A Streaming Approach to Neural Team Formation Training. In the 46th European Conference on Information Retrieval (ECIR), 2024.
pdf doi git reviews ppt video - M.J. Ahmed, M. Saeedi, H. Fani; Skill Vector Representation Learning for Collaborative Team Recommendation: A Comparative Study. In the 25th International Web Information Systems Engineering (WISE), 2024.
pdf doi git reviews - M. Saeedi, C. Wong†, H. Fani; Paradigm Shifts in Team Recommendation: From Historical Subgraph Optimization to Emerging Graph Neural Network. In the 2nd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Information Retrieval in the Asia Pacific (SIGIR-AP), 2024.
pdf doi git reviews ppt video - M. Saeedi, C. Wong†, H. Fani; Collaborative Team Recommendation for Skilled Users: Objectives, Techniques, and New Perspectives. In the 32nd ACM Conference on User Modeling, Adaptation and Personalization (UMAP), 2024.
pdf doi git reviews ppt video - A. Dashti, S. Samet, H. Fani; Effective Neural Team Formation via Negative Samples. In the 31st ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (CIKM), 2022.
pdf doi git reviews - A. Dashti, K. Saxena, D. Patel†, H. Fani; OpeNTF: A Benchmark Library for Neural Team Formation. In the 31st ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (CIKM), 2022.
pdf doi git reviews video - D. Patel†, A. Dashti, K. Saxena, H. Fani; Automating Team Formation Using Machine Learning. Gold Medalist, CAD$300, UWill Discover, University of Windsor, 2022.
link poster - K. Saxena, D. Patel†, A. Dashti, H. Fani; Best Research, CAD$300, Demo Day, School of Computer Science, University of Windsor, 2022.
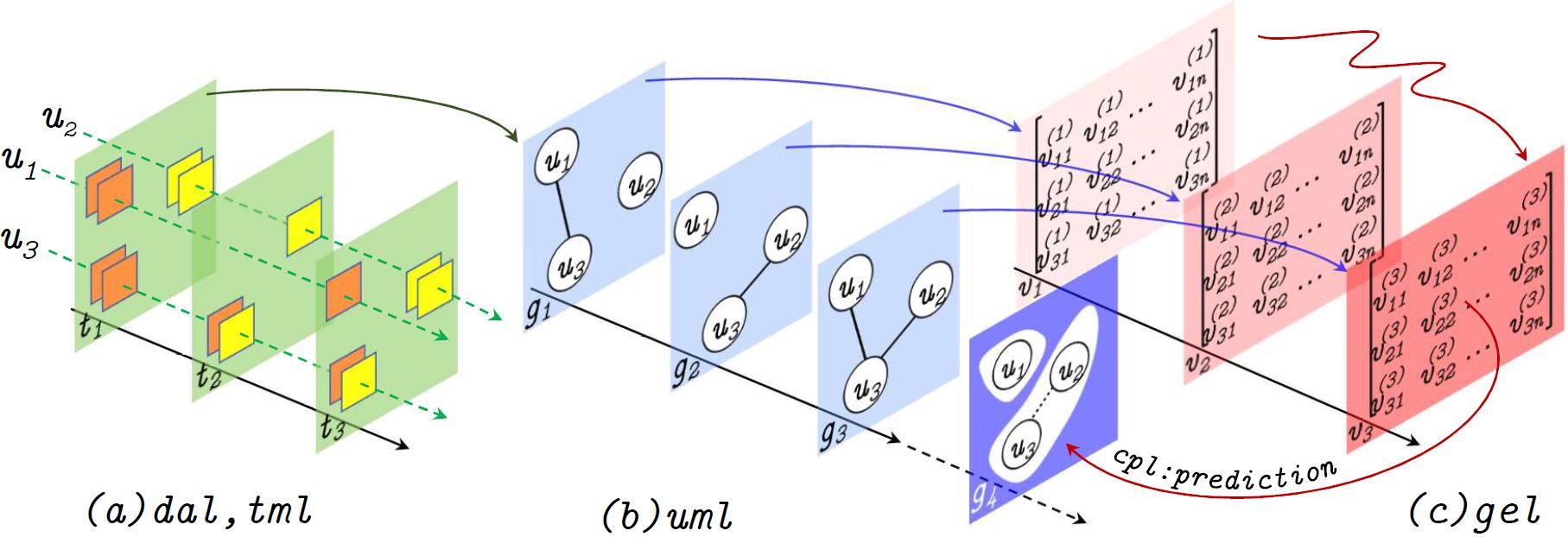
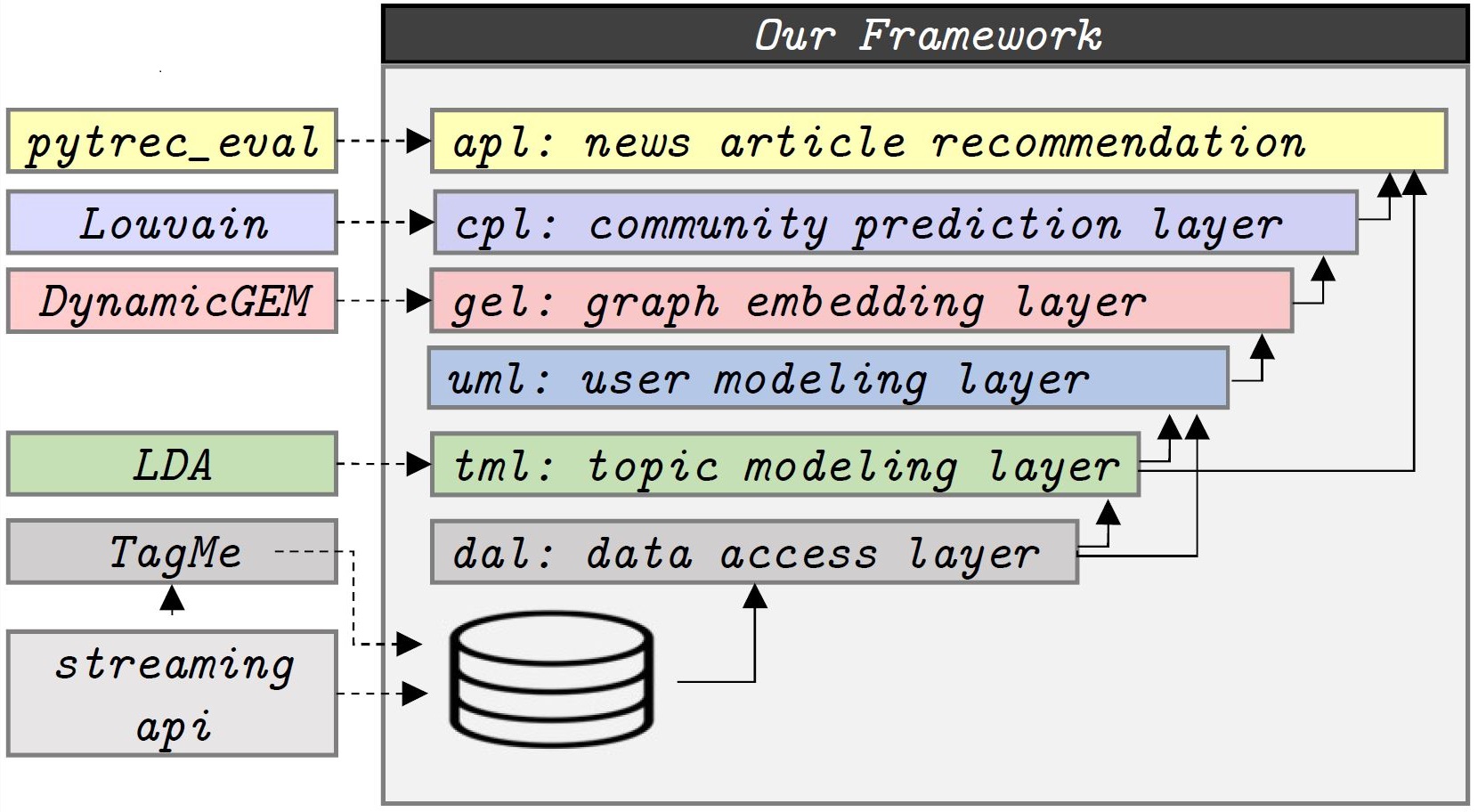
SEERa: Future Community Prediction (2020 - Now)
User community prediction aims at identifying communities in the future based on the users' temporal topics of interest. We model inter-user topical affinities at each time interval via streams of temporal graphs. We benefit from temporal graph embedding methods to learn temporal vector representations for users as users' topics of interests and hence their inter-user topical affinities are changing in time. We predict user communities in future time intervals based on the final locations of users' vectors in the latent space.